RESEARCH & PRODUCTION
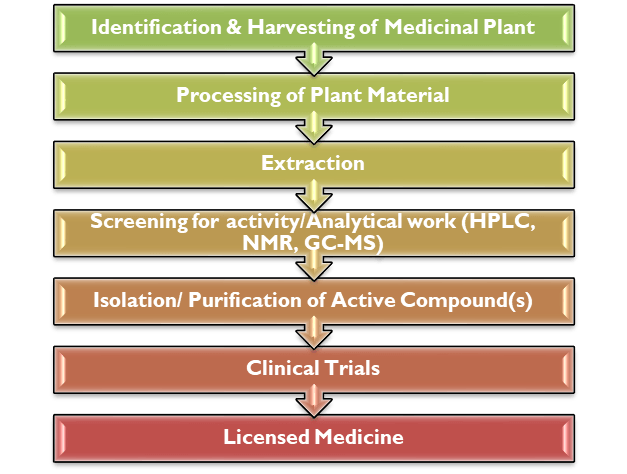
Turning a plant into a standardized medicinal product is a complex process. There is no absolute route, but the process invariably involves the application of specialist techniques including: extraction; separation; analysis; purification; screening and rigorous in vitro and in vivo testing.
Depending on the approach taken, the steps can occur in a different order. The first steps are often based on ethnobotanical research which identifies potential drug candidates, based on traditional use. A raft of legal measures attempt to prevent exploitation of traditional knowledge. Ultimately, very few active compounds from natural sources end up as licensed medicines.
Identification & Naming
The process of creating a natural medicine should begin by determining the species being used. Within a single plant family there are often many genera containing very similar species. Species form the lower level within the (simplified) hierarchical system of natural classification, shown below.
In order to produce a standardized product it is crucial that we know that the plant selected is the species we think it is. We can use several resources to ensure that the plant harvested is correctly identified and to differentiate between species:
Botany
- botanical experts who identify a plant species and assign a botanical (Latin) name.
DNA profiling/Whole Genome Sequencing
- this gives us the genetic fingerprint of a plant species.
Ethnobotany
– a discipline based on the interpretation of knowledge of plant use within different cultures or societies.
Herbarium/Voucher specimens
– carefully chosen plant specimens with identifying information, such as botanical name, time and place of harvesting.
Microscopy
- high powered lenses to visualize a plant's structure and find small but significant differences between species.
Systematics
- the biological classification of plants according to their characteristics and relationships.
Taxonomy
- the study, description and naming of variation between plants or other organisms.
Chemotaxonomy
– the study of chemical variations betwen different plant orders, families and species.
Plant Names
- One of the more challenging aspects of working in natural medicines is the interpretation of plant names. Plant names and naming systems can differ greatly according to culture and many species have multiple common names. To overcome these ambiguities researchers use scientific names – i.e. accepted Latin names from the Linnaean classification model (format: Genus species). Without the consistent application of these names there is always a risk that research and analysis may be based on the wrong plant species.
Cultivation and Harvesting
The expression levels of chemicals within a plant family, species or even its different parts can be assessed using analytical techniques and translated into heat maps or principle component analyses to detect distribution patterns and assist with bio-prospecting – i.e. the search for new medicines from nature.
Cultivation can be summarized as the agricultural preparation of land - e.g. tilling, ploughing and irrigation. Voluntary guidelines are produced by the FDA and United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) to encourage Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) and Good Handling Practice (GHP) as well as stressing the importance of soil quality and climate. Traditional systems often place great importance on the cultivation of medicinal plants in ‘sacred’ locations, time of planting and astrological factors such as moon phase.
Harvesting refers to the gathering of ripe crops (which can be carried out manually or mechanically). Depending on the season, time of day and place of harvesting, the chemical profile of a plant - its chemotype - can vary significantly. Even within the plant itself, different parts (e.g. leaf, root, flower or stem) will contain differing levels of particular chemicals.
Processing
Processing covers a range of measures used to protect material from deterioration during and after harvesting. These may be defined in monographs which set out the legal obligations that govern quality control in the production of natural medicines. Monographs are detailed documents included in pharmacopoeia – literally, drug making manuals - which cover tests for establishing purity, identification methods and storage practices.
Grinding - grinding into a fine powder with a purpose built mill or a mortar and pestle vastly increases the surface area of the sample, allowing more effective extraction to take place.
Processing covers a range of measures used to protect material from deterioration during and after harvesting. These may be defined in monographs which set out the legal obligations that govern quality control in the production of natural medicines. Monographs are detailed documents included in pharmacopoeia – literally, drug making manuals - which cover tests for establishing purity, identification methods and storage practices.
Preparation
Once the correct plant and part has been identified and harvested, the process of preparation can begin. Careful preparation can help to remove contaminants (e.g. heavy metals and pesticides) from a sample. A simple extraction may need very little preparation other than cutting and cleaning. For analytical or commercial purposes preparation is also likely to involve one or more of the following steps:Air drying
- exposure to warm air and ambient heat dries the sample and prevents sample deterioration.
Freeze drying
- removes moisture from the sample at low temperature under a powerful vacuum.Grinding - grinding into a fine powder with a purpose built mill or a mortar and pestle vastly increases the surface area of the sample, allowing more effective extraction to take place.
Extraction
Extraction is the single most important step in obtaining a plant medicine. As plants contain a 'cocktail' of chemicals, extraction requires solvents which help to isolate the desired compounds.In extraction, we are faced with the fact that frequently we are not sure exactly what we are trying to extract. So, extraction strategies are often based on expectations of the potential compound(s) of interest, usually their chemical class and likely polarity.
Solvents
To extract more polar compounds we use a more polar solvent and, for less polar compounds, a less polar solvent. Mid-polar solvents can be used to extract compounds which are neither very highly polar nor of low polarity.
To extract compounds we actually use solvents which are liquids or gases (carriers). Solvents possess different polarities or chemical charges. A compound’s polarity and other physical properties (e.g its pH) determine its affinity with the solvent being used.
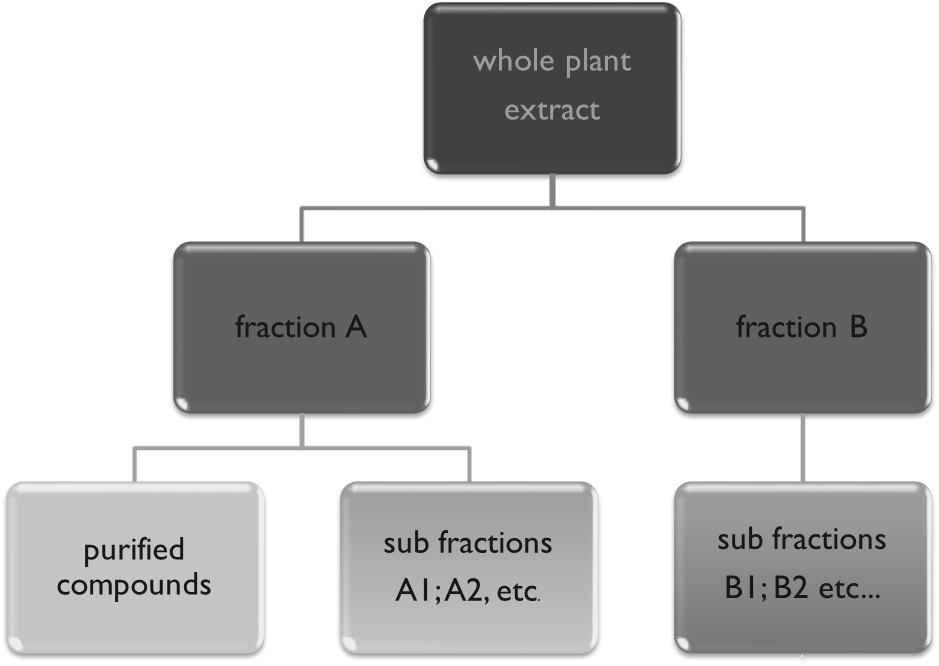
Fractionation
In nature compounds usually exist in a mixture. Fractionation separates a mixture into groups using different combinations of solvents. Once we have a fraction, it can be further divided into smaller and, progressively purer, sub-fractions by using different solvents at each step.
Purification
Purification is the process through which a pure compound is produced – as the name suggests, impurities within fractions are removed and a purified compound can then be confirmed using a range of analytical techniques.
Purification is the process through which a pure compound is produced – as the name suggests, impurities within fractions are removed and a purified compound can then be confirmed using a range of analytical techniques.